Geometry¶

Classes¶
Usage¶
# Disable "Geometry" component.
scons goost_geometry_enabled=no
# Enable "Geometry" component, disable all others.
scons goost_components_enabled=no goost_geometry_enabled=yes
Overview¶
Note
As of now, the component is only available for 2D.
The component provides a GoostGeometry2D singleton with the methods for performing polygon clipping, offsetting (deflating/buffering) and decomposition (triangulation, convex decomposition), as well as providing polypath queries such as polygon area, centroid of a polygon, point in polygon, and generating geometrical shapes at run-time.
The interface is similar to what you can see in the Geometry singleton regarding polygon clipping and offsetting first introduced in Godot Engine 3.2, yet the module brings many other possibilities such as multiple polygon clipping (with holes), building polygon hierarchies, and other specific and hidden features.
Each class of the methods are implemented by their respective back-ends and can be switched at run-time via the ProjectSettings, see below instructions.
Configuring at run-time¶
Switching backends¶
There are a handful of back-ends to choose from:
| Class | Backends | Default |
|---|---|---|
poly_boolean_2d |
clipper6, clipper10 |
clipper6 |
poly_offset_2d |
clipper6, clipper10 |
clipper6 |
poly_decomp_2d |
clipper10:polypartition, polypartition |
clipper10:polypartition |
Differences
clipper6 backend implements both polygon clipping and offsetting. Uses
Clipper 6.4.2
stable version
which is bundled with Godot Engine since 3.2 out-of-the-box.
Experimental clipper10 backend implements most major features which
clipper6 provides, with an additional ability to triangulate the clipping
output. Uses
Clipper 10.0.0 sandbox
version which is still under development.
The polypartition backend takes advantage of the existing
PolyPartition library bundled
with the Godot Engine.
The clipper10:polypartition is an extension to polypartition backend
which provides a more robust triangulation method (handles degenerate polygons),
and shadows an internal bug present in polypartition’s Triangulate_MONO
method.
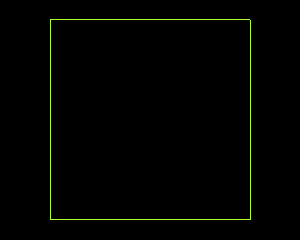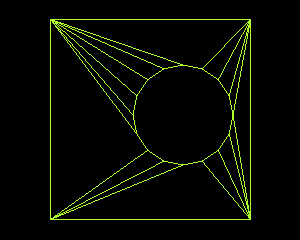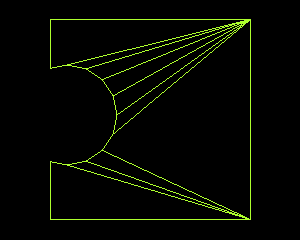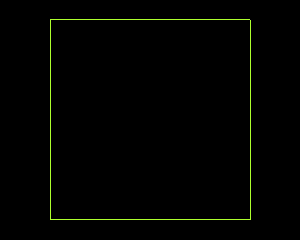
All of these can be set via the goost/geometry options present in the
ProjectSettings (once you open Godot editor the
default settings will be set automatically):